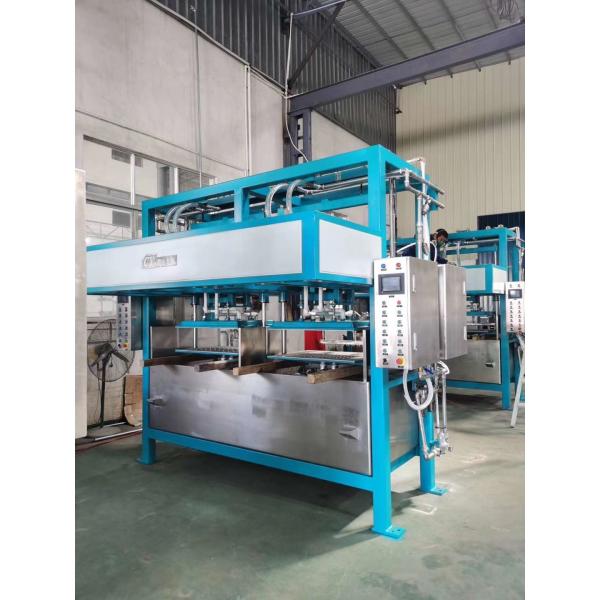
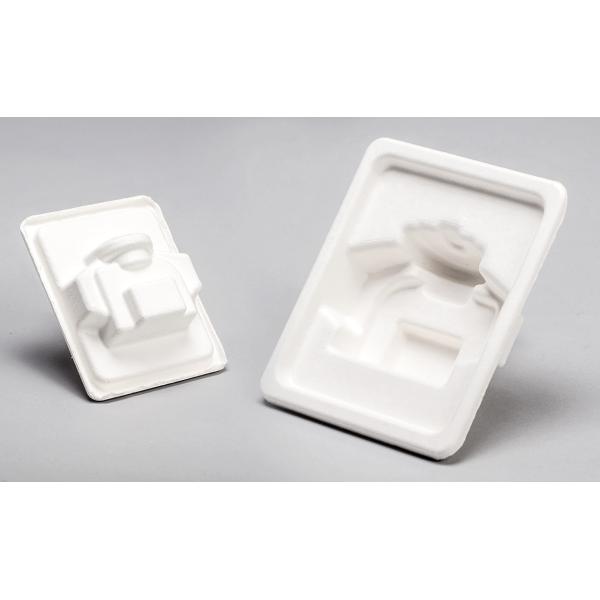
Pollution Free Molded Pulp Industrial Package making machine
Description:
Molding is the process of shaping liquid or flexible raw material by using a rigid structure generally known as mold and the equipment is known as paper pulp molding machine. Recycled paper can be transferred into any desired shape using a mold of that shape. The molding process is applied when a certain shape of the object is to be produced in large quantities.
By using virgin pulp ( surgarcane bagasse, bamboo pulp, wood pulp, straw pulp) , this reciprocating forming machine & wet hot pressing machine are capable of making all kinds of pulp molding industrial package for electronic product, cosmetics products, high-end liquor packaging and crafts, etc
The whole production is under automatic control via HIM, processes of forming, wet hot pressing, and trimming and stacking run continually,
Our machine select high quality electronic devices and pneumatic components and are fully designed by computer assistant engineering and high technology. It has been proven high efficiency, low maintenance and energy saving.
Specification:
| Capacity | 60-250kg/ hr |
| Feeding raw material | Virgin pulp ( bagasse pulp/bamboo pulp/wood pulp/straw pulp) |
| Workshop Requirement | 1000~ 1800㎡ |
| Operator Required | 4 -5 workers/ shift |
| Drying Method | Dry in mold, thermal forming |
| Forming Method | Vacuum forming |
| Electricity consumption | 180-400kw/hr |
| Water consumption | 1-2 tons/hr |
| Control | PLC+ Touch screen |
| Machine Material | All parts in contact with water is SS304 Stainless Steel |
Q & A:
What chemicals are used to make pulp?
Chemical wood pulp is made by cooking wood chips with chemical solutions in digesters operated at elevated temperature and pressure. The chemicals used are (1) sulfite salts with an excess of sulfur dioxide and (2) caustic soda and sodium sulfide (the kraft process).
What are the types of pulping?
There are four broad categories of pulping processes: chemicaly semi-chemical, chemi-me- chanical, and mechanical pulping. These are in order of increasing mechanical energy required to separate fibers (fiberation) and decreasing reliance on chemical action.
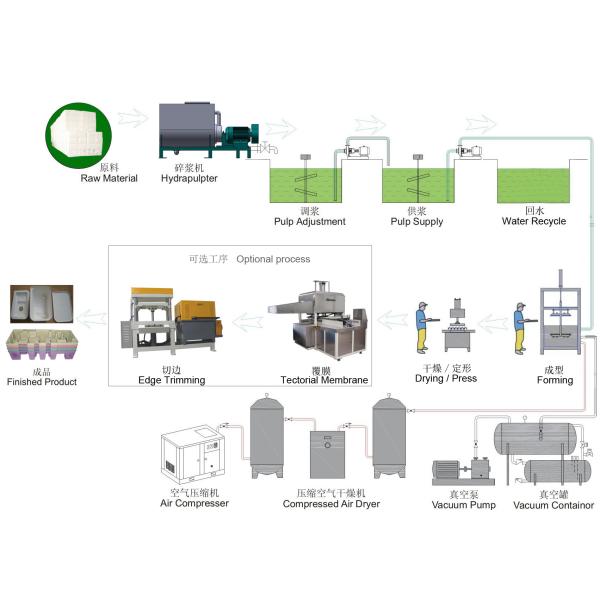
Production Working Process:

Illustrations of Machine & Product: