1 Introduction:
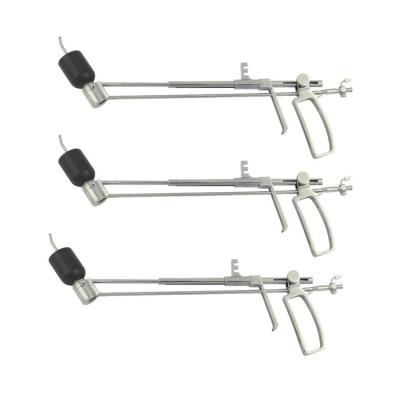
If you are looking for minimally invasive surgery medical instruments with good quality, competitive price and reliable service. Wanhe medcal is manufaturing these for you. We provide general and professional laparoscopic instruments with CE, FDA approved.
2 Specifications
1 Adopt optimum quality stainless steel material
2 Corrosion resistant
3 Tough construction
4 Light weight and easy operation
5 surpeb workmanship
3 Packing & Shipping:
| Package detail: |
Poly bag and special shockproof paper box. |
| Delivery detail: |
By air |
4 Company Show






FAQ
What are the precautions for postoperative care of minimally invasive gynecological surgery?
Postoperative care of minimally invasive gynecological surgery is an important part of ensuring patient safety and promoting recovery. The following are precautions for postoperative care:
Wound care:
Keep the wound clean and dry, observe whether there is redness, swelling or abnormal secretions, and return for regular check-ups
The incision will be covered with a sterile dressing. Please keep the dressing clean and dry. The sutures will be removed or dissolved on their own within 2 weeks
Drainage tube and catheter management:
Properly fix the drainage tube and catheter and keep them unobstructed, observe the color, nature and amount of the drainage fluid, and use an analgesic pump when necessary
The catheter is usually removed within 48-72 hours after surgery. The catheter is clamped 3 days before the removal of the catheter and opened every 2 hours to train the bladder function and restore normal urination ability
Diet management:
After the anesthetic effect subsides, you can resume your normal diet as instructed, but you need to avoid greasy and irritating foods, and supplement high-protein and high-fiber foods to prevent osteoporosis
Fasting for 6 hours in the early postoperative period, after which you can gradually transition to warm liquid food, and then to semi-liquid and regular food
.
Activity and rest:
Getting out of bed and moving as soon as possible helps prevent venous thromboembolism, but be careful to avoid strenuous exercise and lifting heavy objects, especially within 6 to 8 weeks after surgery
.
Bedridden patients should perform limb activities in bed and gradually increase the amount of activity, including participating in self-care
.
Infection prevention:
Perineal disinfection is performed every 6 hours, and patients are reminded not to get out of bed within 6-8 hours after surgery to reduce the risk of infection
.
Antibiotics are used to prevent postoperative infection, generally oral antibiotics for 3-5 days
.
Psychological support:
Nursing staff should take the initiative to introduce the ward environment to patients, help them adapt to the unfamiliar environment, and relieve psychological pressure
.
Spouses should provide spiritual support, both parties should communicate frankly, and pay attention to the time and method of foreplay
.
Complication monitoring:
Closely observe for complications such as bleeding, abdominal organ injury, hypercapnia, subcutaneous emphysema, and pneumothorax
. If there is persistent vaginal bleeding or foul-smelling discharge, pelvic and abdominal pain, chills, fever (temperature above 38°C) or other abnormal conditions, please contact the attending physician or return to the hospital for treatment.
Discharge instructions:
You can take a shower 3-4 days after discharge, but do not rub hard; the time for adnexal surgery and tub bathing depends on the specific situation. intercourse and tub bathing are prohibited for 3 months after hysterectomy.
Regular follow-up, generally considered to be the first follow-up 1 month after discharge, review once every 3 months within 2 years after treatment, review once every 6 months within 3 to 5 years, and review once a year from the 6th year
Through the above meticulous postoperative care measures, the patient's recovery can be effectively promoted, the occurrence of complications can be reduced, and the overall treatment effect can be improved.
What are the best practices for wound care after minimally invasive gynecological surgery?
Wound care after minimally invasive gynecological surgery is a complex and meticulous process that requires a series of best practices to ensure the smooth recovery of patients and reduce the risk of infection. The following are the best practices based on the information I searched for:
Keep the wound clean and dry:
Observe the wound regularly after surgery and pay attention to the cleanliness and disinfection of the wound
Use sterile gauze to cover the wound and keep the dressing clean and dry
The wound should be cleaned every time the dressing is changed to avoid damaging tissue regeneration and re-epidermalization
Timely treatment of exudate and foreign matter:
Regularly flushing the wound can effectively reduce the risk of infection. Removing dead skin, thrombus, necrotic tissue and foreign matter can help reduce the possibility of scarring, adhesion and infection
For open wounds, tetanus antitoxin should be injected to prevent tetanus
Use appropriate suture materials and methods:
Choose appropriate needles and suture materials, and ensure appropriate traction to avoid excessive pressure on the tissue
Decide whether staged sutures are needed according to the condition of the wound, and place drainage to promote wound healing
Antibiotics to prevent infection:
Use antibiotics as prescribed by the doctor to prevent infection. For wounds with signs of infection, local antibacterial therapy and systemic antibacterial therapy can be considered
Functional exercise and early activities:
After surgery, choose the position according to the surgical situation, encourage and assist patients to carry out early activities, and guide patients to carry out limb functional exercises to promote functional recovery and prevent complications.
Gradually increase the amount of activity according to personal physical condition, avoid strenuous exercise and lifting heavy objects to prevent pain caused by vibration.
Psychological support and education:
Provide patient and meticulous education to enable patients to cooperate with the treatment plan as much as possible and ensure psychological support.
Carry out narrative care through listening, analysis and feedback to help patients better understand and cope with various challenges in the postoperative recovery process.
Personal hygiene management:
Guide patients to clean wounds correctly to avoid cross infection.
Wash the vulva at least once a day and observe whether there is secretion and its color, amount and smell.
Avoid improper behavior:
Do not perform vaginal irrigation or use tampons within six weeks after surgery to prevent retrograde infection.
Avoid riding, cycling, vigorous dancing, sitting for a long time and driving to avoid pelvic congestion.
How to correctly fix drainage tubes and catheters to promote postoperative recovery?
Correctly fixing the drainage tube and the urinary catheter to promote postoperative recovery requires comprehensive consideration of various nursing measures. The following are detailed steps and precautions:
1. Properly fix the urinary catheter
Location selection: Fix the urinary catheter on the inner thigh or inner thigh to avoid slipping
.
Fixing method: Use skin-friendly adhesive materials for secondary fixation to prevent slipping, movement, etc.
. When the patient is active, such as getting up or resting in bed, the urinary catheter should be passed over the front of the waistband or above the thigh, and fixed to the bedside with pins and laces
.
Angle and strength: Catheter traction after urethral reunion surgery is conducive to promoting the healing of the separated urethral section. The traction angle is preferably 45° between the urinary catheter and the body axis, and the traction force is preferably 0.5 kg, which is maintained for 2 weeks
.
2. Keep drainage unobstructed
Prevent blood clot blockage: Blood clots are a common cause of catheter blockage and need to be removed in time. Under aseptic operation, sterile saline can be drawn with a syringe to rinse and aspirate blood clots
.
Observe the drainage situation: squeeze the drainage tube regularly to prevent it from being compressed, twisted, blocked or falling out when turning over, observe the color and properties of the drainage fluid, and notify the doctor in time if there is any abnormality.
3. Prevent infection
Strictly perform aseptic operation: change the drainage bag regularly, clean the urethral opening twice a day, and avoid retrograde infection.
Keep the height of the urine collection bag lower than the bladder level: prevent infection caused by urine reflux.
4. Observe and record
Record the drainage situation: record the drainage situation on time every day, including the amount, color, nature and smell, so as to detect abnormalities in time.
Decannulation time: According to the type of surgery and recovery, it is generally retained for 2-4 weeks, but it depends on the specific situation.
5. Strengthen health education
Family cooperation: Strengthen health education for patients and family members, let them actively cooperate with the work of nursing staff, and let family members pay more attention to the fixation of the tube to prevent the catheter from falling off.
In postoperative dietary management, which foods are most helpful in preventing osteoporosis?
In postoperative dietary management, the key to preventing osteoporosis is to consume foods rich in calcium, vitamin D and protein. The following are specific suggestions:
High-calcium foods:
Dairy products: such as milk, cheese, yogurt, etc.
Soy products: such as tofu
Seafood: anchovies, carp, abalone, dried small fish, etc.
Green leafy vegetables: such as Chinese cabbage, kale
Vitamin D:
Food sources: eggs, liver, oily fish (salmon, mackerel), mushrooms
Sunbathing: Sunbathe for about 15 minutes between 10 am and 3 pm every day to promote the synthesis of vitamin D in the body
Protein:
Dairy products: such as milk and dairy products
Meat and beans: lean meat, poultry, whole grain cereals, beans, pods and dried fruits, etc.
Nuts: such as almonds
In addition, the following points should be noted:
Balanced diet: Maintain a balanced diet, avoid excessive consumption of meat and processed foods, and reduce the intake of high-salt, high-sugar, and high-fat foods
.
Supplement phosphorus: The intake of calcium and phosphorus should be maintained at a ratio of 1:1 to improve the efficiency of calcium absorption
.
Limit alcohol and : Excessive drinking and intake of caffeinated beverages increase the risk of fractures
What are the specific measures for infection prevention after minimally invasive gynecological surgery?
The specific measures for infection prevention after minimally invasive gynecological surgery include the following aspects:
Preoperative preparation:
Infection control: Before elective surgery, infections away from the surgical site, such as skin or urinary tract infections, should be carefully identified and treated
.
Blood sugar and blood pressure management: Correct water and electrolyte imbalance, anemia and other problems, control blood sugar levels, and avoid hyperglycemia
.
Antibiotic use: Prophylactic use of antibacterial drugs according to the guidelines, usually used 0.5 to 1 hour before surgery and discontinued within 24 hours
.
Skin preparation: Disinfect the skin with an alcohol-containing disinfectant, avoid shaving one day in advance, and choose a suitable skin disinfectant
.
Intraoperative operation:
Aseptic technique: Strictly abide by aseptic technique principles and hand hygiene standards, ensure that the instruments reach the sterilization level, gently contact the tissue, maintain hemostasis and warming
.
Surgical skills: The surgeon should have superb surgical skills to minimize trauma and bleeding
.
Environmental management: Keep the operating room environment clean, ensure adequate air exchange and positive pressure ventilation, filter all air, and maintain the optimal room temperature of about 21°C
.
Postoperative care:
Hand hygiene: Medical staff should pay attention to hand hygiene and strictly abide by the dressing change process
.
Drainage management: Keep drainage unobstructed, remove the drainage tube in time, observe the incision, and prevent infection
.
Antibiotic application: For patients at high risk of postoperative infection, preventive antibiotics can be considered, but attention should be paid to the problem of drug-resistant bacteria caused by the abuse of antibiotics
.
Observation and follow-up: The patient's surgical site incision should be closely observed after surgery, sent for examination if necessary, and followed up for at least 30 days after surgery
.
What are the psychological support strategies after minimally invasive gynecological surgery?
Psychological support strategies after minimally invasive gynecological surgery include the following aspects:
Preoperative psychological intervention:
Nurses should actively and enthusiastically introduce the hospital situation to patients, create a friendly and active atmosphere, and reduce patients' vigilance and tension
Through face-to-face communication, share successful surgical cases, minimize patients' negative emotions and psychological burdens, and enable patients to welcome surgery in the best state
Answer patients' questions in detail, listen patiently to their complaints and carefully observe their non-verbal behaviors, accurately grasp their psychological reactions and existing problems, and give verbal comfort, support and encouragement
Postoperative psychological counseling:
After surgery, timely discover patients' psychological problems, and actively provide counseling and psychological counseling to help patients relieve negative emotions such as anxiety and depression
On the premise of fully respecting and understanding patients, help patients rebuild their self-confidence through verbal encouragement, comfort, persuasion, etc.
For patients with pain, give abdominal massage, verbal comfort or use painkillers to relieve pain
Application of family system theory:
Nursing staff should meet the requirements of family members to understand information about patients, and make full use of accompanying and family visiting time to educate patients and family members. The husband's approval of hysterectomy plays an important role in alleviating the patient's psychological pressure.
The support of family members is crucial. Nursing staff should obtain the support of the patient's spouse and both parents, correct the idea of "bad luck", let family members take the initiative to care for the patient, and teach them psychological support skills and ways to deal with the patient's negative emotions.
Personalized humanistic care:
Scientifically analyze and formulate nursing plans according to the patient's specific situation, such as communicating with the patient more at work, making the patient feel friendly, natural, and trusting, adjusting the accompanying system, meeting the patient's needs for relatives to accompany, eliminating the patient's concerns, and reducing mental pressure.
Create a good and comfortable treatment environment, strive to foresee the patient's physical and mental requirements, communicate frequently with the patient's relatives and friends, obtain active cooperation, and jointly create a good mental environment for the patient.
Self-psychological adjustment:
Guide patients to conduct meditation and relaxation training to adjust their psychological state, guide patients to take a comfortable lying position, close their eyes, take deep breaths, and relax their muscles in turn. Nursing staff use standardized guiding language to let patients imagine that the operation is very successful, and then the body will gradually recover, so as to achieve the purpose of stabilizing emotions and improving sleep.
Discharge guidance:
For patients with stable conditions and long treatment cycles, attention should be paid to satisfying the need for stimulation. In addition to actively guiding functional exercises, various media should be fully utilized to provide social information, such as providing home wards.
Emphasis on postoperative dietary requirements: eat high-calorie, high-protein foods, strengthen nutrition, eat more fruits and vegetables, and maintain smooth bowel movements; explain precautions for postoperative life
For more photos and details please contact me:
Company Name: Tonglu Wanhe Medical Instruments Co., Ltd.
Sales: Sue