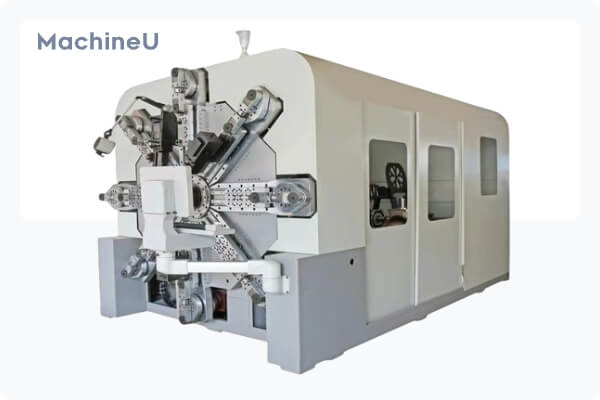
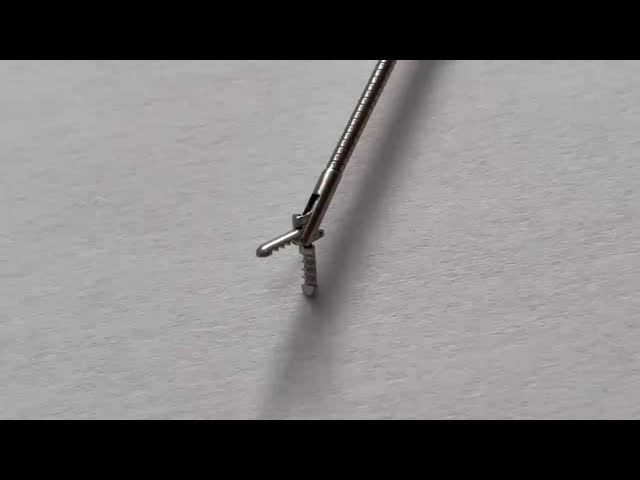
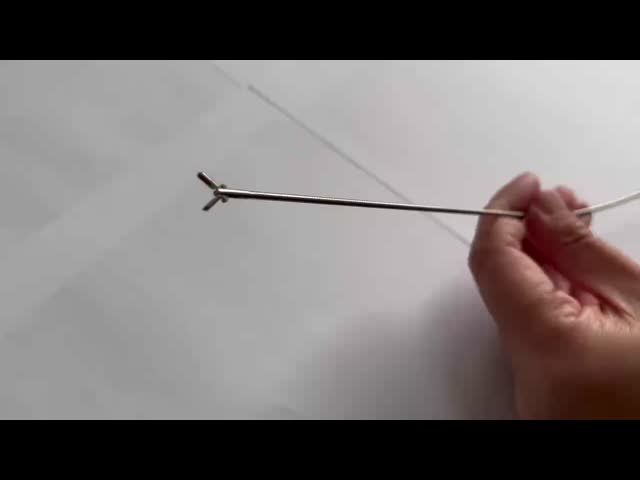
Advanced Phi Rigid Grasping Forceps for Ureterorenoscopy in Adult Urology Instruments
1 Introduction:
If you are looking for minimally invasive surgery medical instruments with good quality, competitive price and reliable service. Wanhe medical is manufaturing these for you. We provide general and professional laparoscopic instruments with CE, FDA approved.
2 Specifications
Adopt 3Cr13, 304, 630 stainless steel material
Tough construction
Corrosion resistant
High durability
3 Packing & Shipping:
| Package detail: |
Poly bag and special shockproof paper box. |
| Delivery detail: |
By air |
FAQ
What is the disinfection and sterilization process for urological surgical instruments?
The disinfection and sterilization process for urological surgical instruments is an important part of ensuring surgical safety and preventing infection. The following is a detailed disinfection and sterilization process:
Cleaning:
Surgical instruments should be initially cleaned immediately after use to remove blood, tissue fragments and other contaminants. This step usually uses warm water and mild detergents or disinfectants.
For instruments with infectious materials, it is recommended to soak them in a 10% bleach solution for 20 minutes.
Enzyme soaking or ultrasonic vibration can further remove difficult-to-remove stains.
Pretreatment:
Put the instruments in a transparent plastic bag for high-pressure steam sterilization, which can remove all macroscopic contaminants.
For items that cannot withstand high temperature and moisture, ethylene oxide sterilization is preferred.
High-pressure steam sterilization:
Heat-resistant and moisture-resistant surgical instruments should be sterilized by pressure steam first, and chemical disinfectants should not be used for immersion sterilization.
The sterilization temperature is generally 134°C and the duration is 5 minutes.
High-pressure steam sterilization is suitable for most metal instruments and some plastic products.
Chemical sterilization:
For instruments that are not resistant to high temperatures, such as soft endoscopes (cystoscopes, fiberscopes, etc.), 2% glutaraldehyde can be used for more than 30 minutes for disinfection.
Ethylene oxide is an effective low-humidity sterilization method, especially suitable for rubber and plastic products.
Low-temperature plasma sterilization:
Some modern equipment such as electric knives and electric cutters need to be sterilized by high-temperature steam, while low-temperature plasma sterilizers are used for instruments that cannot withstand high temperatures.
Boiling disinfection:
This method is less used because it causes the greatest damage to surgical instruments and significantly shortens their service life. It is suitable for metal instruments, syringes, glass products and rubber instruments. The specific method is to put the packaged instruments into a boiling sterilizer and boil them at 100℃ for 15-30 minutes (killing general vegetative bodies) or 1-2 hours (killing spores or spores).
Inspection and packaging:
The sterilized instruments need to be inspected to ensure that there are no residues and oiled for protection.
When packaging, it should be noted that instruments of different materials and types should be stored separately to avoid cross contamination.
Storage and transportation:
The sterilized instruments should be placed in a designated area to avoid moisture or interference, and detailed information including the sterilization date, sterilizer number, cycle number, load control record, exposure time and temperature should be recorded and saved.
Through the above steps, the urological surgical instruments can be effectively cleaned and sterilized thoroughly, thereby ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the operation.
What are the latest standards and specifications for the disinfection and sterilization of urological surgical instruments?
The disinfection and sterilization standards and specifications for urological surgical instruments are mainly based on the following aspects:
Sterilization requirements:
The sterilization requirements for surgical supplies, sharp instruments and infusion equipment are detailed in the "Technical Specifications for Disinfection of Medical and Health Institutions". For example, surgical sutures can be sterilized by ethylene oxide gas or rapid pressure steam sterilization; ordinary scalpels, scissors and other sharp instruments need to be sterilized after decontamination and washing; heat-resistant surgical supplies such as pacemakers and artificial valves can only be sterilized by cold sterilization or chemical sterilization.
Diagnostic and treatment instruments, instruments and articles that enter the sterile tissues, organs, cavities of the human body, or come into contact with damaged skin, mucous membranes and tissues of the human body should be sterilized.
Use and inspection of disinfectants:
The general requirements for medical device disinfectants are clearly stipulated in GB/T 27949-2020, including the determination of physical and chemical indicators, validity period, microbial killing effect, metal corrosion, compatibility of disinfectants and instruments, continuous use stability and toxicological safety.
Management of external medical devices in the operating room:
Before use, external medical devices should be cleaned, disinfected, sterilized and monitored by CSSD in accordance with the provisions of WS310.2 and WS310.3; after use, they should be cleaned and disinfected by CSSD before they can be returned.
Prevention measures for infection:
Disinfection and sterilization of laparoscopic surgical instruments in urology is one of the important links in preventing surgical site infection. In addition, the doctor's intraoperative operation is also a key factor.
Other relevant standards:
Surgical personnel must strictly follow the "Medical Personnel Hand Hygiene Standards" to perform surgical hand disinfection and ensure that the surgical instruments, instruments and items used reach the sterilization level.
What are the comparative studies on how to evaluate the effects of different disinfection methods on urological surgical instruments?
The comparative studies on the effects of different disinfection methods on urological surgical instruments mainly involve the following aspects:
In urological surgery, commonly used sterilization methods include high-temperature and high-pressure steam sterilization. This method has the advantages of reliable sterilization effect and simple operation. In addition, indicators such as surgical site infection rate and sterilization effect should be monitored to evaluate the application effect of operating room sterilization methods and monitoring.
The current operating room instrument disinfection and sterilization evaluation method is poorly compatible with automated cleaning equipment, resulting in low accuracy of evaluation results. To address this problem, an operating room instrument disinfection and sterilization evaluation method based on automated cleaning equipment was designed. The information entropy algorithm was used to obtain the indicator information volume, and disinfection and sterilization evaluation indicators were added.
No instrument contamination occurred during the centralized disinfection and sterilization process, indicating that the centralized cleaning, disinfection and sterilization effect was ideal. The effect of disinfection and sterilization can be further improved by improving work processes, improving professional skills, and focusing on quality supervision.
For the cleaning and disinfection of the surface of objects in the operating room, different methods (such as 75% ethanol, chlorine-containing disinfectant, and clean water) are used for wiping and disinfection. The sterilization rate of each group can be compared, so as to find a reasonable cleaning and disinfection method.
The researchers compared the effects of different disinfection methods through experiments and proposed some new disinfection methods. For example, ultrasonic disinfection is a new physical method that can use ultrasonic vibration to break bacteria and viruses.
Although boiling disinfection is less used because it causes the greatest damage to surgical instruments and significantly shortens their service life, it is still suitable for metal instruments, syringes, glass products, and rubber instruments. The specific method is to put the packaged instruments into a boiling sterilizer and boil them at 100°C for 15-30 minutes (to kill general vegetative bodies) or 1-2 hours (to kill spores or spores).
Based on the above, the comparative study on the effect of different disinfection methods on urological surgical instruments needs to be conducted from multiple perspectives, including the selection of appropriate sterilization methods, the use of automated cleaning equipment for evaluation, the quality analysis of centralized cleaning and disinfection, the comparison of the effects of different cleaning and disinfection methods, and the research progress of new disinfection methods.
Application of ethylene oxide sterilization in urological surgical instruments and its safety evaluation report.
The application of ethylene oxide sterilization in urological surgical instruments and its safety evaluation report are as follows:
Application
Ethylene oxide sterilization is a disinfection method commonly used in the medical industry, especially for surgical instruments that are not resistant to high temperature and moisture. According to the research of the Hebei Provincial Health Commission, ethylene oxide gas can produce non-specific alkylation with microbial proteins, DNA and RNA, thereby achieving significant sterilization effects. In addition, the research of Nanning Maternal and Child Health Hospital in Guangxi showed that ethylene oxide sterilizers can keep items sterile for a long time, safe and effective, and are especially suitable for the sterilization of instruments that are not resistant to high temperature and high heat.
In actual applications, for example, Cook Urology's Peel-Away, which is designed to be inserted into the urinary system for interventional diagnosis or treatment, is sterilized with ethylene oxide. This shows that the application of ethylene oxide sterilization technology in urological surgical instruments is widespread and effective.
Safety Assessment
Although ethylene oxide sterilization has a significant sterilization effect, there are certain risks and challenges in its use. First, ethylene oxide itself is highly toxic, so environmental conditions need to be strictly controlled during operation to avoid occupational exposure risks. Secondly, ethylene oxide sterilizer equipment must be equipped with pressure relief, fire relief and explosion-proof devices to ensure the safety of the equipment.
According to an evaluation report from Baidu Library, no safety issues such as gas leakage and harmful gas emissions were found through on-site monitoring and monitoring by air detection instruments. This shows that under standardized operation and strict monitoring, the ethylene oxide sterilization process is relatively safe.
In addition, the national standard GB/T 18279-20XX has detailed the relevant requirements for ethylene oxide sterilization of medical devices, including considerations of action time, temperature, humidity and other factors, as well as the evaluation of the impact of multiple sterilizations on the product. These standards provide a scientific basis for the safety and effectiveness of ethylene oxide sterilization.
Conclusion
In general, the application of ethylene oxide sterilization in urological surgical instruments is effective and widespread, especially for precision instruments that are not resistant to high temperatures and high heat. However, due to the strong toxicity of ethylene oxide, environmental conditions need to be strictly controlled and corresponding safety measures need to be taken during its use.
What are the efficiency and limitations of low-temperature plasma sterilization technology in the disinfection of urological surgical instruments?
The efficiency and limitations of low-temperature plasma sterilization technology in the disinfection of urological surgical instruments are as follows:
Efficiency
High efficiency:
Hydrogen peroxide low-temperature plasma sterilization has the highest sterilization efficiency and its sterilization time is relatively short. For example, simple instruments can be sterilized within 30 to 50 minutes, while complex instruments require 50 to 70 minutes.
Studies have shown that hydrogen peroxide low-temperature plasma sterilizers are better than ethylene oxide gas sterilization for sterilization supply room instruments, and have higher utilization and turnover rates.
Economical:
Compared with other low-temperature sterilization methods (such as ethylene oxide), the cost of hydrogen peroxide low-temperature plasma sterilization is relatively high, but its fast and efficient characteristics make it more advantageous in some cases.
Safety and convenience:
This technology does not require special environmental conditions, such as neatness, water, and special ventilation and drainage systems. It only requires ordinary voltage to operate, and has excellent safety and convenience.
Limitations
Limited scope of application:
Existing low-temperature plasma technology has limitations such as small discharge range and high discharge voltage, and is not suitable for disinfection and sterilization of large-sized medical devices.
Although the system can handle metal and non-metal products, there may still be applicable restrictions for some special materials or large instruments.
Cost issues:
Although hydrogen peroxide low-temperature plasma sterilization has excellent efficiency, its cost is high and may not be suitable for all medical institutions.
Biological monitoring qualified rate:
In actual application, although there was no significant difference in the biological monitoring qualified rate between the two groups, the observation group was superior to the control group in terms of sterilization time, sterilization effective time, adverse event rate and medical staff satisfaction.
Low-temperature plasma sterilization technology shows high efficiency and good economy in the disinfection of urological surgical instruments, especially suitable for heat-sensitive and high-turnover medical devices.
What are the studies on the effects of boiling disinfection on metal and plastic urological surgical instruments?
The studies on the effects of boiling disinfection on metal and plastic urological surgical instruments mainly focus on the following aspects:
Metal instruments:
Boiling disinfection is suitable for metal instruments, which need to be boiled in water to 100°C for 15 to 20 minutes.
This high-temperature treatment can effectively kill microorganisms, but it should be noted that most metal instruments are not corrosion-resistant, so rust may occur after boiling. In addition, chlorine-containing disinfectants are highly corrosive to metals. If chlorine-containing disinfectants are used for cleaning and sterilization, special attention should be paid to anti-rust measures.
In terms of long-term preservation, the ATP fluorescence test pass rate of metal instruments sterilized by high-pressure steam sterilization was 97% after 8 months, indicating that it has a good preservation effect.
Plastic instruments:
For plastic materials, especially high-performance medical-grade plastics such as TECASON P MT (PPSU), it has excellent resistance to common sterilization techniques, including hot steam sterilization. However, some plastic materials may not be suitable for boiling sterilization because boiling may cause deformation or damage.
Plastic materials such as PVC cannot affect their performance after sterilization and disinfection processes such as dry heat disinfection, wet disinfection, chemical treatment, and radiation disinfection, which shows that different types of plastic materials have different adaptability to disinfection methods.
Boiling disinfection has certain applicability and limitations for both metal and plastic urological surgical instruments. For metal instruments, although boiling can effectively kill microorganisms, care should be taken to prevent rust and corrosion;
For more photos and details please contact me:
Company Name: Tonglu Wanhe Medical Instruments Co., Ltd.
Sales: Emma
Tel:+86 571 6991 5082
Mobile: +86 13685785706